SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
Hyra Network is a specialized Layer 3 chain designed for high-throughput AI workloads, decentralized compute coordination, and micro-transaction settlements.
It inherits:
- Security from Ethereum (L1)
- Scalability from Base (L2)
- Low-cost Data Availability via the AnyTrust model
Hyra Network focuses on how transactions are processed, how system components interact, and how finality is achieved.
Layered Architecture Overview
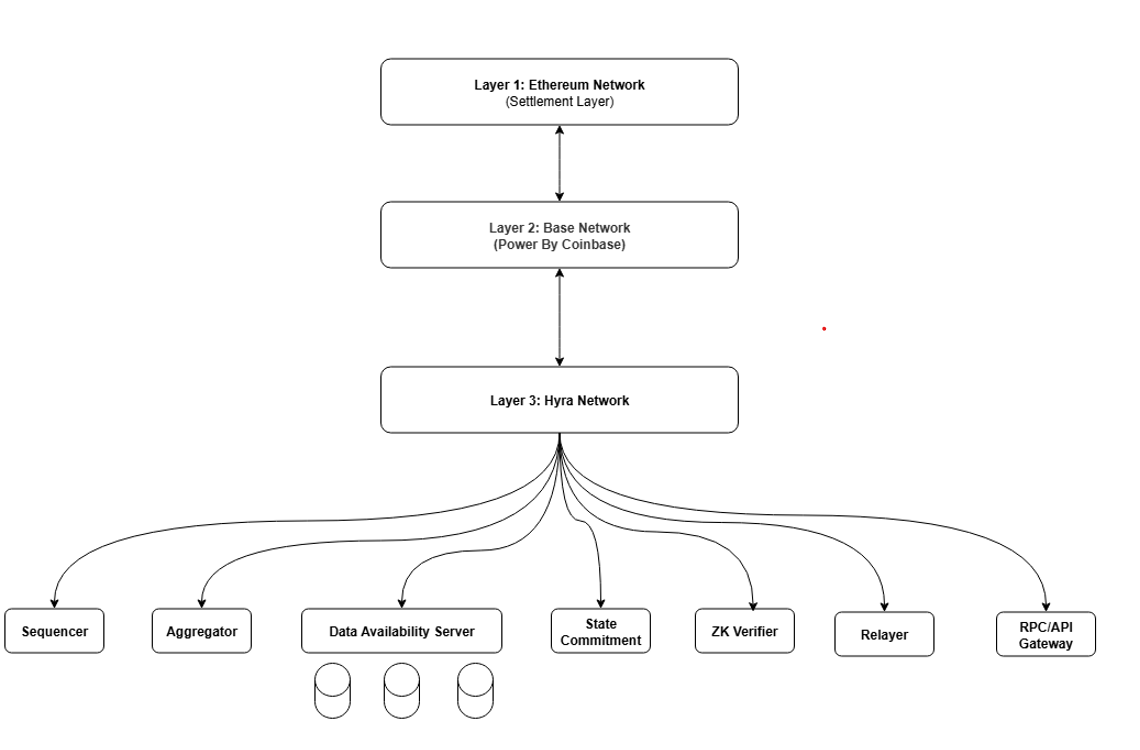
Hyra Network operates within a 3-layer structure, but in this page we focus on the roles they play inside Hyra’s system, not their internal technology.
Layer Responsibilities (Hyra Perspective)
-
Layer 1 — Ethereum:
Final settlement, fraud-proof anchoring, security guarantees. -
Layer 2 — Base:
Executes verification logic for Hyra’s batches, handles bridging, inherits Ethereum security. -
Layer 3 — Hyra Network:
Execution, sequencing, smart contracts, AI & compute orchestration.
🔧 Core System Components (Hyra L3 Infrastructure)
Below are the actual components that make Hyra Network function.
This is the core of the System Architecture page.
1. Sequencer
The Sequencer is responsible for:
- Receiving user transactions
- Ordering them deterministically
- Building L3 blocks
- Providing fast confirmations
- Forwarding block data to the Aggregator
Deployment:
- 1 active
- 1 hot-standby (instant failover)
2. Aggregator
Role:
- Collects L3 blocks from the sequencer
- Compresses them into batches
- Prepares metadata + proofs
- Sends to Base (L2) for verification
- Uses AnyTrust signatures from DAC
- Falls back to Rollup DA if DAC unavailable
3. Data Availability Committee (DAC / DAS)
Each DAC member:
- Stores full batch data
- Signs the batch hash
- Ensures cheap data availability (AnyTrust mode)
- Triggers fallback if quorum fails
Hyra uses this to achieve low-cost L3 execution while keeping safety guarantees.
4. State Commitment Contract (on Base L2)
Tracks:
- L3 state roots
- Batch confirmations
- Fraud windows
- Rollup fallback logic
This contract ensures verifiable state transitions.
5. ZK Verifier (Optional Future Module)
Ox supports future enhancements:
- Zero-knowledge proofs
- ML model attestation
- ZK compute proofs
Not required today but already part of long-term architecture.
6. RPC / API Gateway
Provides public access for:
- Wallets
- DApps
- Indexers
- AI task coordinators
Supports:
- JSON-RPC
- WebSocket
- Load balancing
- Mempool queries
- Traces & logs
🧱 Data Flow — End-to-End
- User sends transaction → RPC
- Sequencer orders & executes transactions
- Aggregator batches L3 blocks
- DAC signs batch data (AnyTrust)
- Aggregator posts batch metadata → Base
- Base finalizes → inherits Ethereum L1 settlement
This results in a secure, low-cost, high-throughput Layer 3 execution pipeline.
📘 Conclusion
Hyra Network’s system architecture is designed for:
- AI-driven workloads
- Extremely low fees
- Fast confirmations
- High-throughput micro-transactions
- Guaranteed security via Base + Ethereum
- Guaranteed data availability via AnyTrust + Rollup fallback
This makes Hyra a next-generation chain optimized for AI & decentralized compute.